Rapid 3D Printing Services
Fast, Accurate Solutions for Your Prototypes
- 20+ Years of 3D Printing Expertise
- Diverse Material Choices
- Rapid Turnaround Times
- Precision Down to ±0.05mm
What is Rapid 3D Printing?
Rapid 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, transforms digital 3D models into physical parts by depositing material layer by layer. This technology accelerates prototyping, enables custom production, and supports small-batch manufacturing, making it ideal for industries requiring speed and precision.
How It Works (Overview):
- Upload your 3D file (e.g., STL or OBJ).
- Select material and printer settings.
- Build layer by layer with precision.
- Finish with cleaning, curing, or polishing, then inspect.
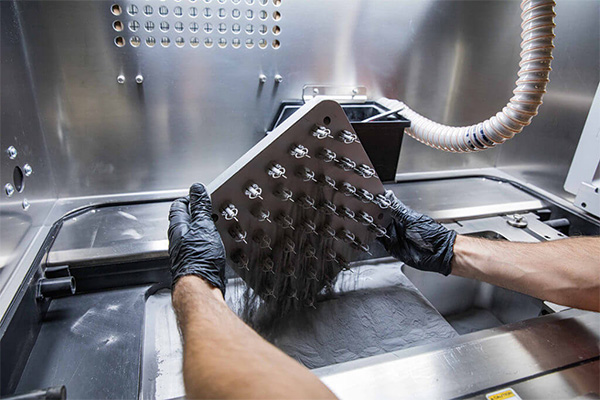

Why Choose XTJ for Your 3D Printing Needs
Discover XTJ’s 3D printing solutions, specializing in rapid 3D printing services, 3D printing prototypes, fast 3D printing solutions, and high-precision 3D parts. With over 20 years of expertise, we excel in custom 3D printing and quick turnaround 3D manufacturing, delivering tailored results for your projects. Our state-of-the-art facilities and dedicated team ensure you get reliable, high-quality parts on time, every time.
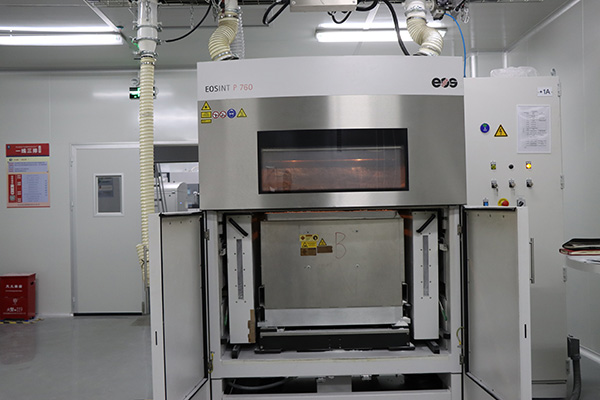
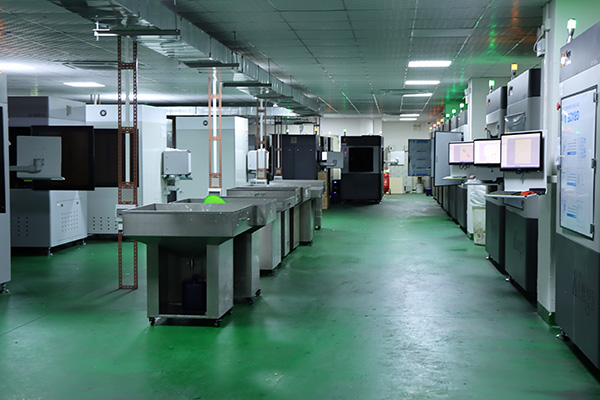
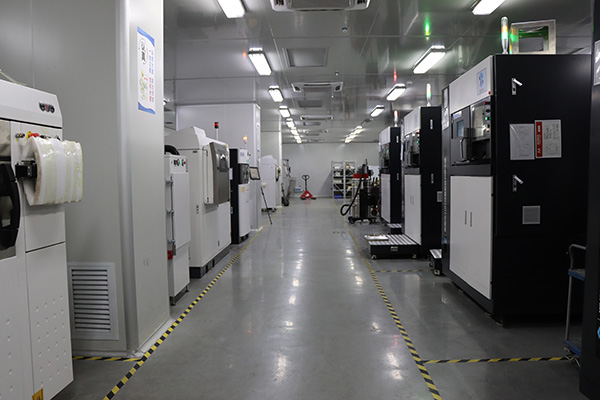
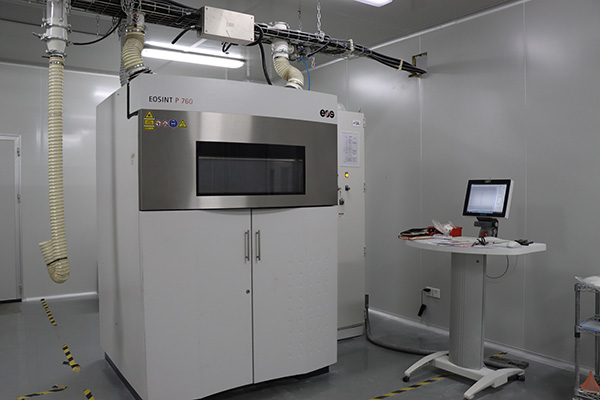
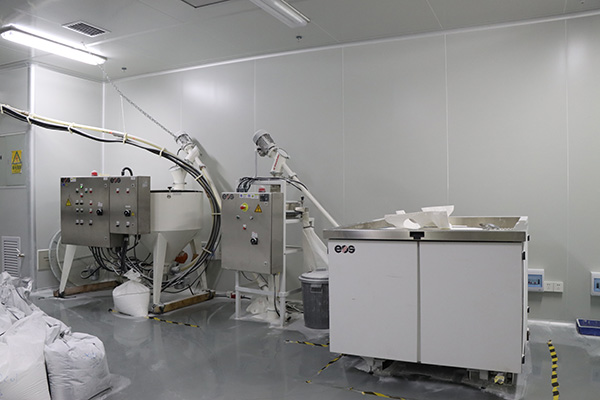





Our Advanced 3D Printing Technologies
XTJ leverages three cutting-edge methods to meet diverse project needs:
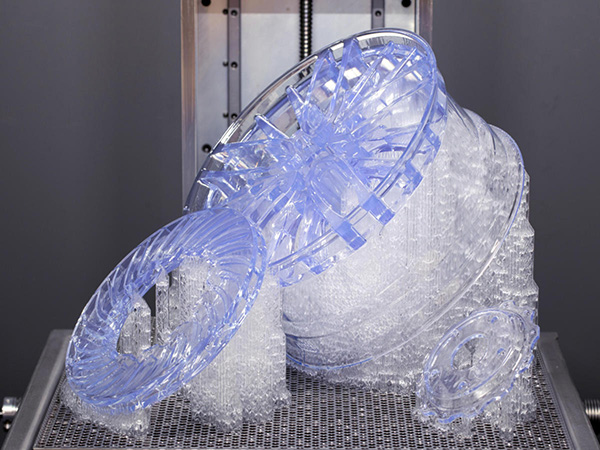
High-Resolution 3D Printing SLA utilizes a laser to cure liquid photopolymer resin into solid layers, offering exceptional surface finish and detail. The build platform descends into a resin vat, where the laser selectively hardens each layer, creating intricate parts. This technique excels in applications requiring fine features.
Prozess:
- Fill a vat with photosensitive resin.
- Laser cures layers with 0.025–0.1mm thickness.
- Lower the platform and repeat until complete.
- Wash and cure under UV light for final hardening.
- Advantages: Superior resolution (down to 0.025mm), ideal for detailed models like jewelry or dental applications.

Reliable and Cost-Effective 3D Printing,FDM builds parts by extruding melted thermoplastic filaments, such as PLA or ABS, through a heated nozzle onto a build platform. The nozzle moves in precise patterns, layering material to form durable components. This method is widely used for functional prototypes and tooling due to its affordability and strength.
Prozess:
- Heat filament to a molten state (180–250°C).
- Extrude through a nozzle with 0.1–0.4mm precision.
- Layer deposition based on the 3D model.
- Cool and remove supports, then apply finishing.
- Advantages: Cost-efficient, suitable for robust prototypes, large build volumes up to 400x400x500mm.
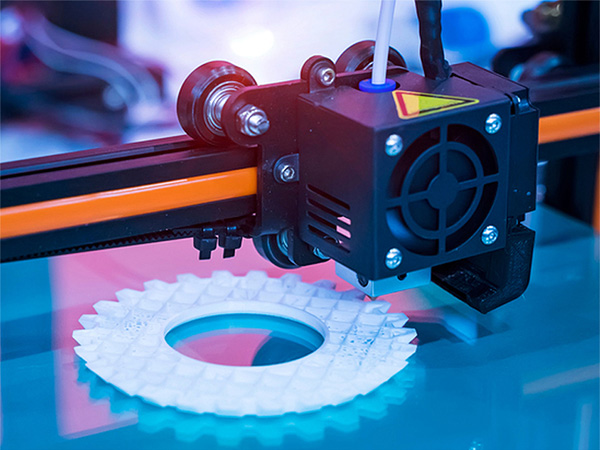

Durable and Complex 3D Printing SLS employs a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or metal, into solid parts. A thin layer of powder is spread, and the laser sinters it according to the design, building robust components layer by layer without support structures. This method suits functional parts with complex geometries.
Prozess:
- Spread a 0.06–0.12mm layer of powder.
- Laser sinters the powder at high temperature.
- Add subsequent layers and repeat.
- Remove excess powder and clean the part.
- Advantages: High durability, versatile for functional parts, build volume up to 340x340x600mm.
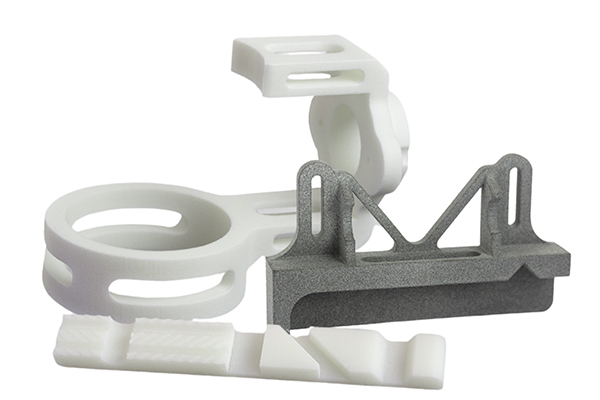
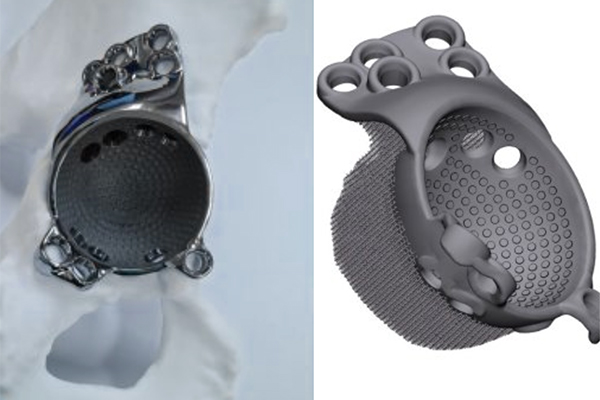
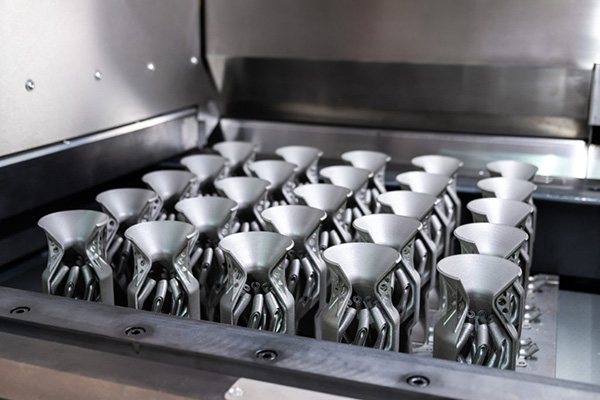
XTJ offers a wide range of materials and applications to support your projects
- Thermoplaste: PLA, ABS, PETG (strong and cost-effective).
- Photopolymers: cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.
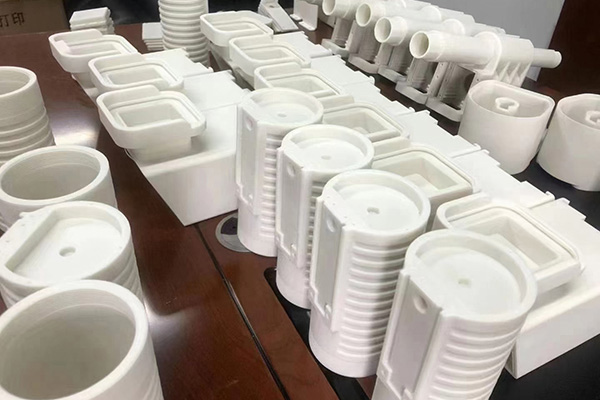

cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
| Merkmal | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| Materialien | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| Anwendungen | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. | Gears, Functional Parts |
| Layer Thickness | 0.1–0.3mm | 0.025–0.1mm | 0.06–0.12mm |
| Build Volume | 400x400x500mm | 300x300x400mm | 340x340x600mm |
| Am besten geeignet für | Cost-Effective Prototyping | High-Detail Applications | Durable, Complex Designs |
Enhance Your 3D Printing Outcomes
Use STL or STEP with solid models.
Keep walls at least 1.5mm thick.
Add supports for angles over 45°.
Request sanding or painting for a polished look.
Engineered for Speed and Quality
FDM, SLA, and SLS printers.
Zeiss CMM for precision checks.
Deliveries in as little as 24 hours.
Custom solutions for your designs.
3D Printing vs. CNC Machining: Which is Better for Your Prototypes and Production?
Understanding 3D Printing and CNC Machining
3D printing and CNC machining are two powerful manufacturing technologies, each with distinct strengths. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, excels in producing small batches of parts without the need for molds, allowing for rapid turnaround and low costs. It requires minimal human intervention, enabling automated production. The cost of 3D printing is determined by the amount of material used, meaning larger parts or higher quantities can increase expenses. On the other hand, CNC machining, a subtractive process, is more complex. It requires specially trained engineers to pre-program machining parameters and tool paths, followed by automated production based on those instructions. This preparation adds labor costs to the quotation, but CNC machines can operate continuously without supervision, making them highly suitable for large-scale production.
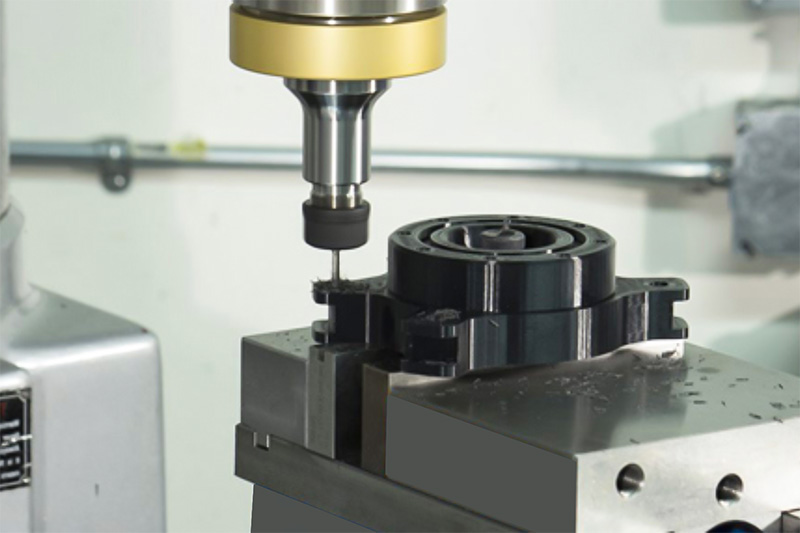

Comparing 3D Printing and CNC Machining
Here’s a detailed comparison to help you decide which technology best fits your prototyping or production needs:
Merkmal | 3D Printing (Additive) | CNC Machining (Subtractive) |
Prozess | Builds layer by layer from digital designs | Cuts material from a solid block |
Materialien | Plastics, Resins, Metals (limited) | Metals, Plastics, Composites (wide range) |
Geschwindigkeit | Fast for prototypes (24–48 hours) | Slower setup, better for high volumes |
Kosten | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
Komplexität | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
Oberflächenfinish | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
Am besten geeignet für | cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
