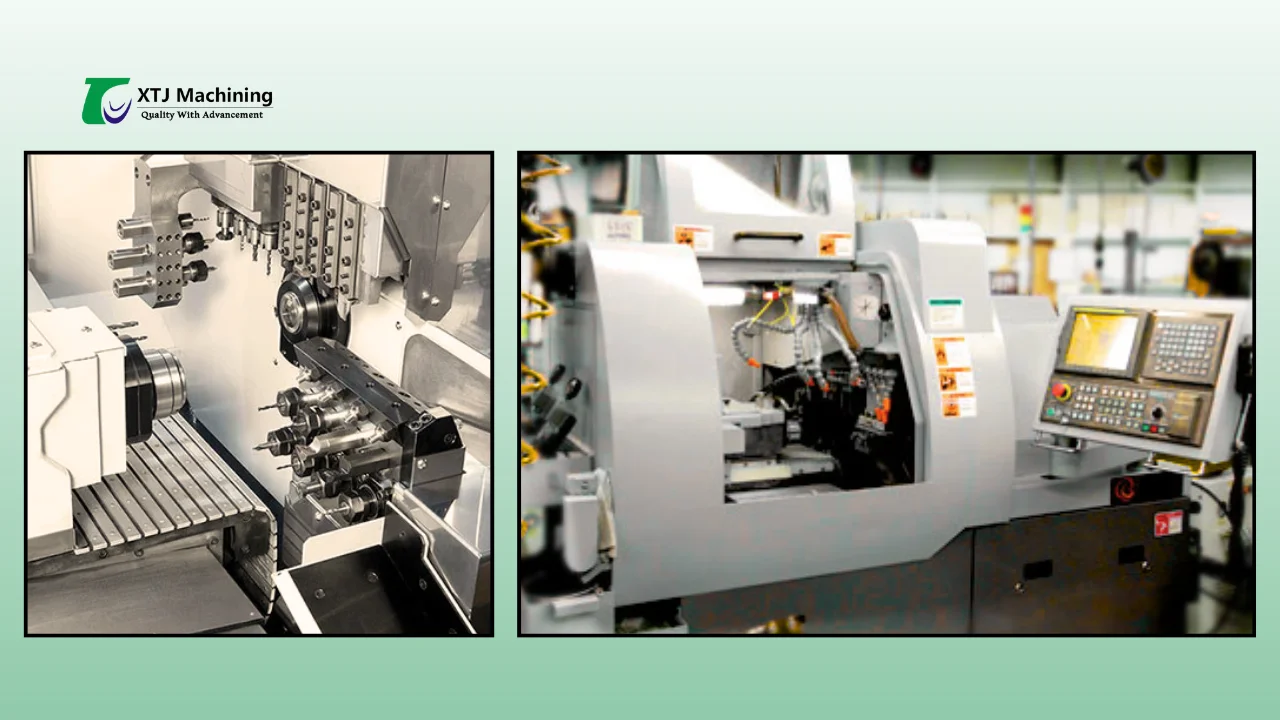
What is Swiss Machining? A Deep Dive into the Process
Swiss machining, also known as Swiss turning, is a precision machining process designed for producing small, complex parts with tight tolerances. Unlike conventional turning, Swiss machining uses a sliding headstock that moves the workpiece axially, guided by a fixed guide bushing close to the cutting tools. This setup allows the workpiece to be supported near the cutting area, minimizing deflection and enhancing accuracy.
Core Mechanics and How It Works
- Sliding Headstock: Moves the bar stock longitudinally through a fixed guide bushing.
- Guide Bushing: Holds and supports the part close to the cutting area, reducing vibrations.
- Multiple Tools: Positioned on a turret to perform simultaneous operations like turning, milling, drilling, and tapping.
- High-Speed Spindles: Allow machining of complex shapes from sliding the bar while multiple tools engage simultaneously.
Key Specifications and Capabilities
| Specification | Swiss Machining Detail |
|---|---|
| Maximum part length | Typically up to 12 inches (300 mm) |
| Part diameter range | 0.008″ to 1″ (0.2 mm to 25 mm) |
| Допуски | ±0.0001″ (2.5 microns) |
| Production volume | Ideal for high-volume production |
| Tooling complexity | Supports multi-tool simultaneous use |
| Материалы | Metals like stainless steel, titanium, brass, and plastics |
Pros and Cons of Swiss Machining
Плюсы:
- Extremely tight tolerances and superior surface finishes
- Excellent for long, slender parts due to guide bushing support
- High-volume production with consistent quality
- Ability to perform complex multi-process operations in one setup
Минусы:
- Limited to small diameter parts
- Higher initial machine cost and tooling investment
- Setup can be time-intensive for low volume or prototypes
Swiss machining shines in precision manufacturing, especially for medical devices, aerospace components, and electronics, where accuracy and miniaturization are critical. Its unique mechanics enable unmatched control over small, complex parts that are difficult to machine with traditional CNC turning.
What is Multi-Axis Milling? Mastering Complex Geometries
Multi-axis milling is a CNC machining process that uses multiple rotational axes to cut and shape materials into complex parts. Unlike traditional 3-axis milling, multi-axis CNC machines typically operate with 4, 5, or even more axes, allowing the cutting tool to move around the part from different angles. This capability is essential for creating intricate designs and precise features that simple milling can’t handle.
Core Mechanics and Axis Breakdown
- 3-Axis Milling: Moves the tool along X, Y, and Z axes (left-right, forward-back, up-down).
- 4-Axis Milling: cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
Key Specifications and Capabilities
| Особенность | Описание |
|---|---|
| cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| cURL Too many subrequests. | Металлы, пластики, композиты |
| Допуски | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| Максимальный размер детали | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| Обработка поверхности | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
Плюсы и минусы
Плюсы:
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
Минусы:
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
Multi-axis CNC milling is a game-changer when you need detailed parts with complex geometries, making it a popular choice for precision machining in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Swiss Machining vs. Multi-Axis Milling
When deciding between Swiss machining and multi-axis milling, understanding their key differences can help you target the right process for your project. Here’s a quick breakdown and an easy-to-read table to compare their specs and ideal uses.
Ultimate Comparison Table
| Особенность | Swiss Machining | Multi-Axis Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Основной процесс | Sliding headstock, guide bushing for precise turning | CNC milling with 3-5+ axis tool movement |
| Лучше всего подходит для | Small, tight-tolerance parts with complex turning features | Complex 3D shapes and contours, multi-surface milling |
| Typical Part Size | Small to very small (micro parts common) | Small to large parts, depending on machine size |
| Точность | Extremely high, tight tolerances (±0.0001″) | High precision, especially in surface finish |
| Объем производства | High-volume, consistent production runs | Low to medium volume, prototyping, complex parts |
| Общие применения | Medical devices, aerospace components, watch parts | Aerospace panels, automotive molds, prototypes |
| Setup & Programming | Moderate complexity, focused on turning operations | Complex programming for multiple axes and tool paths |
| Tool Access | Limited to turning and some milling on small diameters | Full access to multi-directional milling and drilling |
| Материалы | Metals like stainless steel, brass, titanium | Wide range including tough metals and composites |
Visual Breakdown
- Swiss machining excels with tiny, cylindrical parts where precision and volume matter. The sliding headstock and guide bushing hold the part firm, making it perfect for turning complex shapes like watch gears or implant components.
- Multi-axis milling is your go-to for cutting complex 3D surfaces, with machines moving around multiple axes to carve out sophisticated shapes, ideal for aerospace parts or detailed molds.
When to Choose Each
- Pick Swiss machining if:
- You need very tight tolerances on small diameters.
- The job involves long production runs with minimal variation.
- Parts are predominantly round or tubular with detailed turning needs.
- Pick Multi-Axis Milling if:
- The part has complex 3D geometry requiring detailed surface work.
- Production volume is lower or you need rapid prototyping.
- You want flexibility for different materials and shapes.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests. как максимально использовать преимущества ЧПУ-обработки нержавеющей стали.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- Swiss Machining
- Идеально подходит для cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests. жесткие допуски.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- Multi-Axis Milling
- cURL Too many subrequests. сложными геометриями cURL Too many subrequests.
- Machines handle a variety of jobs but may need longer cycle times, increasing labor costs.
- Setup might take longer, especially for multi-operation parts, but tooling costs tend to be moderate.
- Great for lower to medium volume runs where versatility matters.
Volume Discounts and Cost Estimator Tool
- Swiss machining often benefits from significant volume discounts; the more you produce, the better the rate per piece.
- Multi-axis milling pricing can be steadier regardless of volume but may offer project-based discounts depending on complexity.
- Using an online cost estimator tool can help you quickly compare these variables based on your part size, complexity, and order quantity.
What to Watch for in Your Budget
- Tooling and setup charges
- Machine run times and cycle efficiency
- Post-processing or secondary operations
- Quality assurance and inspection costs
By breaking down these costs early, you’ll get a clearer picture of which process fits your budget and project demands better.
Common Challenges and How XTJ Solves Them
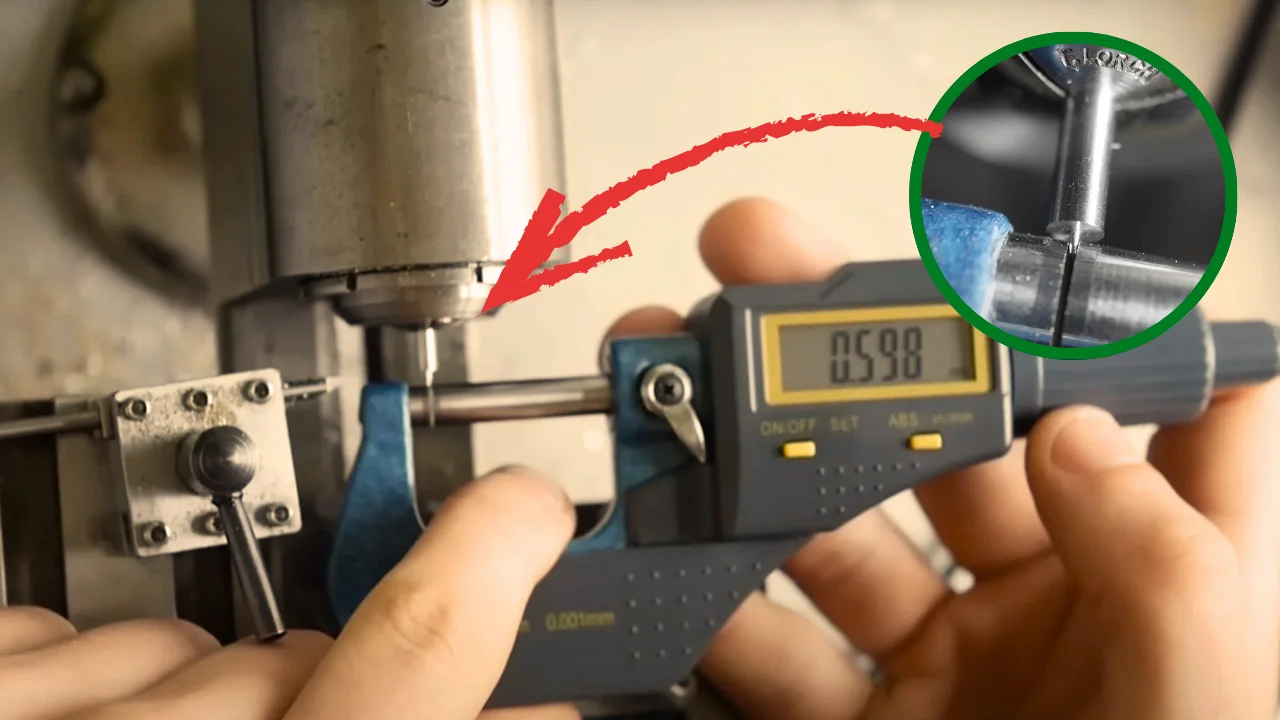

When it comes to Swiss machining and multi-axis milling, a few common challenges pop up: vibration, tooling issues, and maintaining tight quality control. These challenges can affect precision and efficiency—but that’s where XTJ Precision Mfg shines.
Tackling Vibration
Vibration is a big one in high-speed CNC machining. It can lead to surface imperfections and shortened tool life. XTJ uses advanced machine calibration and vibration-dampening technology, ensuring smoother cuts and consistent results. This means your parts hit exact tolerances every time.
Tooling Troubles Made Simple
Tool wear and breakage slow down production and add cost. XTJ’s tooling experts carefully select cutting tools matched to your material and design needs. Plus, they monitor tool performance in real time to swap out or recondition tools before issues occur. This proactive approach keeps your project moving without surprises.
Quality Control That Doesn’t Miss a Beat
Precision machining demands tight quality control. XTJ uses in-line inspection systems and rigorous final checks, identifying any flaws early. Whether it’s Swiss turning or multi-axis CNC milling, they guarantee parts meet your specs with zero compromise.
XTJ Expertise and Assurance
XTJ’s experienced team combines years of machining know-how with state-of-the-art equipment. This ensures your parts are not just made, but made right. The company’s commitment to continuous improvement and customer communication means challenges are solved quickly and effectively.
By managing vibration, optimizing tooling, and enforcing strict quality control, XTJ Precision Mfg delivers precision parts that live up to the toughest demands in aerospace, medical, and high-volume manufacturing industries.
FAQs: Swiss Machining vs. Multi-Axis Milling
Q: What’s the main difference between Swiss machining and multi-axis milling?
Swiss machining uses a sliding headstock and a guide bushing to support long, thin parts during high-volume turning, perfect for tight tolerances. Multi-axis milling, on the other hand, moves the tool across multiple axes to shape complex geometries from a solid block, handling more diverse shapes but often at a slower pace for small parts.
Q: Which method is better for small, precision parts?
Swiss machining typically wins for small, precision cylindrical parts like aerospace components because of its tight tolerance control and efficient high-volume production.
Q: Can multi-axis milling handle complex shapes better than Swiss machining?
Yes. Multi-axis CNC milling excels with complex shapes and multiple angles since it can move on 3, 4, or 5 axes, making it ideal for parts requiring detailed, multi-surface machining.
Q: Is Swiss machining more cost-effective for large runs?
Generally, yes. Swiss machining is highly efficient for large production runs of small, precise parts, reducing labor and cycle time. Multi-axis milling can be more costly for volume but offers flexibility for prototype or varied parts.
Q: What industries use these technologies most?
Swiss turning is popular in medical, aerospace, and electronics for small, precise parts. Multi-axis milling is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery where complex shapes and strong materials are common.
Q: Are there hybrid solutions using both techniques?
Absolutely. Some manufacturers combine Swiss machining for initial turning with multi-axis milling for finishing, optimizing both precision and complexity.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.