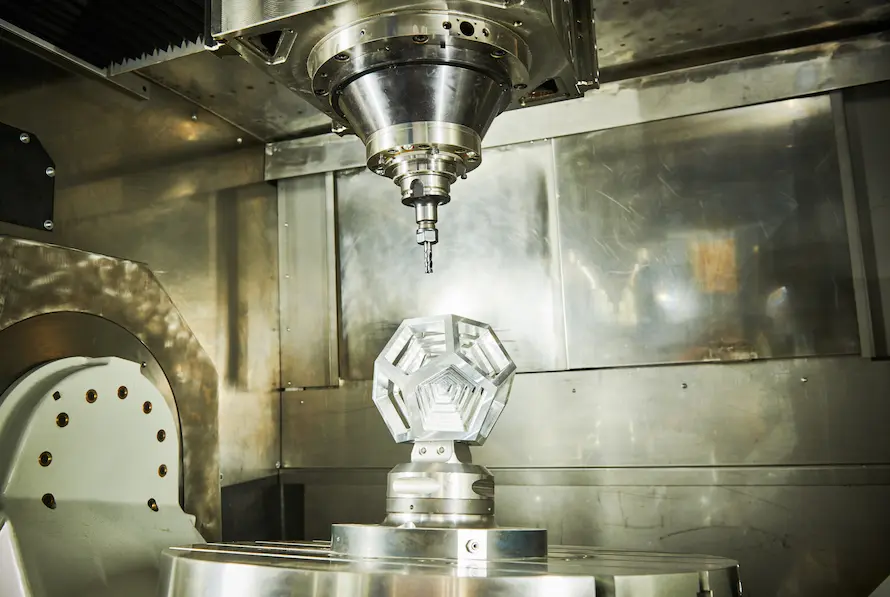
In the last few years, the advancement of multiaxis machining have become somewhat of a standard in most industrial operations. As manufacture develops more and more, catering to wider functionalities of machines and demands that are more complex, it capitalizes on the need to improve quality of manufacturing services, performance of equipment as well as the overall ability to produce complex parts and components, for a cost effective price and efficiency.
This constant cycle of development has essentially increased the expected output of manufacturing processes and industry in general. As such, the development of multiaxis machining has followed a somewhat similar pattern. Enabling a CNC milling machine to operate on additional axes quickly became the prominent challenge. Whereas the transition from 3-axis to 5-axis CNC machines revolutionized several aspects of manufacture with the single setup and enabling surface-independent machining, 6 axis machines are more distinct. This machining process is largely known for its ability to produce more complex shapes in a time efficient way. Yet, there is more to 6 axis CNC machines, and what largely made them a significant change in industry.
What Is a 6 Axis Machine
To understand what distinguishes 6 axis CNC machines, it’s important to look at how they relate to a wider array of multiaxis CNC machines. The number of axes refers to the combined total of translational and rotational axes. 3-axis CNC machines enabled the cutting or milling to move along three translational axes (x, y, z) with no rotation. 5-axis CNC machines on the other hand operate on two additional rotational axes for the workpiece (rotation along the x and y axes). 6 axis machines are distinguished by the additional rotational axis that the cutting tool is enabled rotate along.
The additional rotational axis definitely improves the output and accuracy of 6 axis CNC machines. Although most multiaxis CNC machines can operate different tool head parameters (lathe, cutting tool, mill), 6 axis machines have the advantage of seamlessly operating these tool head parameters with increased speeds, notably for CNC routers.
The process of these machines is significantly improved over the 5-axis CNC machining method, and is quite efficient, optimal for high volume operations, and can significantly reduce cutting time and increase productivity.
Difference From Other Multiaxis Machines
With an additional axis, the 6 axis CNC milling machines differs from other multiaxis machines by an increased capability for detailed designs and complex shapes. This is mainly further empowering the main strengths of multiaxis machines. The ability to rotate and move the several components along all possible axes allows a CNC or milling machine to produce seemingly any type of complex geometries and seamlessly transition from one mode or tool head parameter to another.
Indeed, the additional axis on a CNC machine determines its complex shape machining capabilities, by the main advantage of 6 axis machines of other configurations, is not only the ease of production of complex geometries, rather the speed and the machine’s ability to significantly decrease production times. Several industrial use cases have reported a 75 % cut in production time when using a 6 axis machine. They are designed to achieve maximum precision, and maintain the same alignment, grip and seamless use. This is especially true in high volume operations, where it is the optimal choice, and almost a standard, as they can produce larger parts in less time.
There are many parts and geometries that would have been impossible in a 5 axis CNC machine, or at least time consuming. This means that 6 axis machines are equipped to do much more of the applications enabled by multiaxis machining in general.
6 Axis Machining Routers
Most multiaxis CNC machines can operate a router as a tool head parameter. This piece of equipment consists of a flat base with an extending blade, and can hollow out an area in hard material. CNC routers can operate in a wide range of hard materials like metal, cast iron, aluminum and others. In addition, CNC routers can do much of the tasks performed by several workshop tools like boring machines and spindle moulders.
CNC routers can work at much higher speeds in 6 axis machines. This enables 6 CNC routers to produce much larger parts without surface fixtures in the sides of the workpiece. This is why this configuration is largely used to produce molds for the production of industrial parts and components. A 6 axis CNC and milling machine, with increased performance on many tool head parameters, can seemingly produce any type of component regardless of its shape complexity, size or volume constraints.
Applications of 6 Axis CNC Machines
6 axis machines are relied upon to produce parts and components for several industries. Notably, large parts and very complex and sensitive components that are hard to produce, or impossible, with the help of other multiaxis CNC milling machines. This would usually exclude or medium sized parts or moderately complex or non-cylindrical geometries. Nonetheless, the obvious advantage in terms of precision of 6 axis machines, coupled with its speed and reduced production times make it an optimal choice for many uses, with more complex projects that are exclusively the specialty of 6 axis CNC machines.
Aerospace
As an industry known for high demand in highly complex and expensive parts, usually made them from very solid material, the aerospace relies on 6 axis CNC machines. Besides the complexity and tight tolerances required of engine components, 6 axis machines are also used to produce helicopter blades. Aircraft wings in particular can sometimes be massive reaching up to 24 meters (80 ft), requiring the use of some specialized 6 axis machines. Military aircraft also contain components that require the precision of 6 axis CNC machines.
Automotive
This industry has long relied on 6 axis CNC machines to make models that would be used to build parts and components for automobiles. Because of its ability to produce complex pieces with precision in a short time, 6 axis CNC machine have become widely relied upon in the automotive industry, where excellent quality components, as well as large pieces, are constantly mass required.
Medical
In this sector, the advent of 6 axis CNC machine has enabled a larger scale production of many pieces and parts that were previously seldom produced, either because of their complexity, size or the time required to produce it in excellent quality. Artificial bones for examples are often inspected at a higher degree of quality control. The level of detail and amount of work required to produce artificial bones, although feasible with a other configuration but 6 axis CNC machines are significantly more efficient and cost effective. Custom pieces with highly detailed specifications are quite common in the medial industry, and they largely required the fast and minute motions of 6 axis CNC machines.
Advantages And Limitations
6 axis CNC machines have a clear advantage over configurations with fewer axes. The precision and high speed of 6 axis CNC machines can obtain complex shapes and highly customized pieces in excellent condition. The addition of a 6 axis CNC machine can significantly increase its productivity. The entire process of multiaxis machining is more streamline; a benefit that is accentuated by 6 axis CNC milling machines. There are many aspects in which a 6 axis CNC machine is inherently superior to other configurations. For these types of usage, a 6 axis CNC machine will improve the quality and productivity, otherwise it would require a complicated process involving several machines. Other projects however can only be possible, or cost-effective in an industrial setting, with the use of 6 axis CNC machine.
Despite their obvious advantage, there are some limitations to the potential of 6 axis CNC machine. By design, they are often used mainly for high scale or volume operations. This is due to the high cost of 6 axis CNC machines. The current advances in industry and technology are further enabling the capabilities of 6 axis CNC machines, and making this technology more available. However, for now, this is still a costly piece of equipment, with very high capabilities.
Conclusion
Nowadays, the 6 axis CNC machines is still a marvel of modern engineering. Indeed, this piece of equipment further enables the potential of multiaxis machining and has the potential to transform manufacture. The high cost and demand for skilled workers to operate are still some of its major limitations. This is however offset by the developing demand for high quality manufacture of complex parts, enabling the production of innovative pieces of technology.