Undercutting is a sophisticated machining process that has its roots in chemical machining techniques. Originally, this method involved the use of chemical etchants to penetrate materials laterally, forming a recessed cavity beneath the surface, known as an undercut. Transitioning from chemical to mechanical means, undercut machining today utilizes mechanical tools to carve out these specialized cavities.
This article aims to illuminate the intricacies of the undercut machining process, including its evolution, various methodologies, and practical applications.
Table of Contents
What is Undercut Machining?
Standard straight-cutting tools efficiently cut through the top layer to form a desired cavity. However, they are not suitable for creating cavities adjacent to or underneath these surfaces due to their linear motion and shape. This limitation necessitates a specialized cutting technique to achieve those types of cuts.
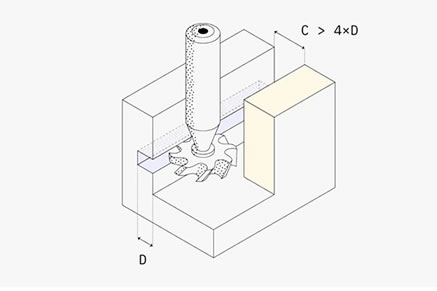
T slot undercut machining
Undercut machining is a peculiar machining process to create recessed surfaces within mechanical components. These CNC machined parts with undercuts usually have a surface extending over another.
To understand undercuts, imagine the shape of a T-slot. The horizontal part of the “T” represents the undercut. Although the top of the slot is easily accessible and can be machined with standard tools, the horizontal undercut—extending inward and parallel to the surface—cannot be reached directly from above.
Undercuts can be external or internal. External undercuts, often found in molds, are relatively simpler to machine because they are more accessible. On the other hand, internal undercuts are hidden within components and are more challenging to create. These are commonly found within gear hubs, where a part of the surface dips beneath another.
How Dose Undercut Machining Works
CNC undercut machining is a challenging process that requires customized processes, and specialized tools.
how end mill cutters make undercuts
Here’s a detailed note on how machinists can create undercut in machining:
Step 1: Understanding the Geometry
The first step involves a thorough analysis of the component’s geometry. Examine the profile to determine if the undercut is internal or external. Document the machining strategies required and the sequence in which they should be applied to achieve the intended design.
Step 2: Selecting the Right Tools
There is no one-size-fits-all tool for undercut machining; each job demands a specific CNC undercut tool. Select tools based on the material and the specific profile and depth required.
Step 3: Setting Up the CNC Machine
Prepare the CNC machine by inputting the detailed design specifications through the CAD software. Attach the specially designed spindle for undercut machining and securely clamp the material onto the work table.
Step 4: Machining Process
The addition of tool and clamping of the workpiece is critical, the CNC machine takes care of the rest. It automatically cuts the material as per the defined path.
Step 5: Quality Control
The final step in the process is a comprehensive inspection of the machined part. Verify that all dimensions are within the specified tolerances and the desired range. This quality control check ensures the undercut meets all design requirements and the part functions as intended.
Importance of Undercut in Modern Manufacturing
In most cases, we want to avoid the use of undercut in the design. However, when we want to achieve functional and design objectives, their use becomes unavoidable. For instance, undercuts are instrumental in enabling the interlocking and seamless assembly of components, particularly in designs that demand secure locking mechanisms without the reliance on external fasteners.
Moreover, undercuts also aid in weight reduction, especially in the aerospace industry, where each gram counts towards fuel efficiency and payload capacity. This technique aids in the crafting of internal cavities that maintain strength while eliminating unnecessary material elsewhere.
Undercuts are also a part of most hydraulic systems. They serve as essential pathways for fluids, creating channels and spaces needed for the guided movement of liquids or gases.
In some cases, especially in CNC turning, undercuts occur at the end of the threaded section of a shaft to provide clearance for the cutting tool as it transitions to a lower cross-section.
Common Types of Undercuts in Machining
Undercut is typically a sunken or recessed surface in a machined part. It could have different profiles in different applications. Based on that geometric profile, there are multiple types of undercuts:
T-slot Undercut
A T-slot undercut has a ‘T’ shape. Such a cavity is usually made for holding parts together with a T-shaped fixture. The head of the bolt gets inside the slot and can slide along the length for fixation.
T-slot undercut is made in two steps. Initially, the standard end mill cutter makes a slot. Next, a specialized tool (T-slot cutter) makes the T-shape. T-slotter has a vertical shaft called a shank and a cutting blade perpendicular to the shank. This blade starts from the cross-section of that earlier slot and cuts undercut in the horizontal direction. T-slot cutter is usually customized through CNC turning for the job nature. However, generally available tool widths are between 3 to 35mm.
One-sided Undercut
A one-sided undercut specifically targets one surface of a workpiece. These undercuts are for scenarios where a component requires a precision groove on one side to accommodate specific assemblies, especially seals or retaining rings.
A lollipop cutter, which has single-side cutting, is used for making a one-sided undercut. This lollipop is clamped to a multi-axis CNC which moves the tool around the periphery of the workpiece, where the cut is required.
Dovetail Undercut
A dovetail undercut is purely for joining two components. The dovetail undercut features an angled blade design with two parts: one wedge section and the other recessed section. The wedge assembly securely locks itself in the recessed part, securing the two parts together.
This undercut is quite common in the woodworking industry. Here, the cutting tool has slightly tapered edges, with angles between 45° and 60°.
Tapered Undercut
A tapered undercut has a sloping surface that tapers from one side to another. This type of undercut is particularly beneficial in applications where you need a tight, frictional fit between two parts, such as in mechanical assemblies, or where the aesthetic of a smoothly tapering surface adds value to the final product.
Machining tapered undercuts involves using tapered end mill cutters, designed to precisely carve the undercut’s gradual slope.
Threaded Undercut
Threaded undercuts feature internal threads, as in screws and bolts. They are essential for parts that need screwing. Specialized thread mills and taps are used for adding threads to undercut parts. The thread mills carve the thread path in a helical motion and are suitable for both internal and external threading.
Spherical Undercut
These undercuts have a 3D curved surface resembling a sphere. The spherical undercuts feature in parts requiring rotary motion, such as ball joints or bearings.
Ball-nose end mills aid in machining these curved undercut shapes. These end mills have a rounded tip that allows for the efficient cutting of curved profiles through a programmed CNC path.
Keyway Undercut
Keyway undercuts serve a specific purpose: to house a key that locks two mechanical parts together and prevents them from rotating independently of each other. We machine these undercuts in shafts or other rotational components that transmit torque. A gearing system is a perfect example.
Machinists use broaches or keyway cutters to create these slots. A broach is a tool with a series of progressively larger teeth, used to remove material through a linear motion, creating a precise slot or keyway in one pass. Whereas, a keyway cutter is similar to a T-slot cutter. It is inserted into a milling machine, where it rotates to remove material and form the slot.
Relief Undercut
A relief undercut is often created around bearings or shafts. Here, a small groove or recess is cut into parts to reduce stress concentrations or provide clearance.
Standard undercut end mills or slotting cutters can machine these undercut profiles. The cutter moves along the predetermined path around bearings or shafts, removing material to create a groove. This operation may require multiple passes to achieve the exact depth and shape.
O-ring Groove Undercut
This groove is specifically cut to house an O-ring, creating a tight seal between the two parts. Specialized O-ring groove cutters ensure the precise dimensions and placement of the groove. They help prevent leaks in various applications.
Technical Insights of Different Undercuts
Let’s get some more technical details on these undercut types, and explore their key applications, tooling, and challenges.
XTJ is a leading OEM Manufacturer that is dedicated to providing one-stop manufacturing solutions from prototype to production. We are proud to be an ISO 9001 certified system quality management company and we are determined to create value in every customer relationship. We do that through collaboration, innovation, process improvements, and exceptional workmanship.

