Injection Molding Services
Need to quickly test out the market with low-volume parts? Or want to create large quantities of production parts? Then you can’t go wrong with our injection molding services. At XTJ, we produce high-quality prototype moldings from aluminum molds with quick turnaround times. Our customers can test out their designs for manufacturability and functionality, fast. We also offer plastic injection molding for your high-volume production needs.
Whether you need rapid tooling, mass production mold making or end-use plastic molding with tight tolerances, our team of experienced specialists can offer a cost-effective solution at each stage.
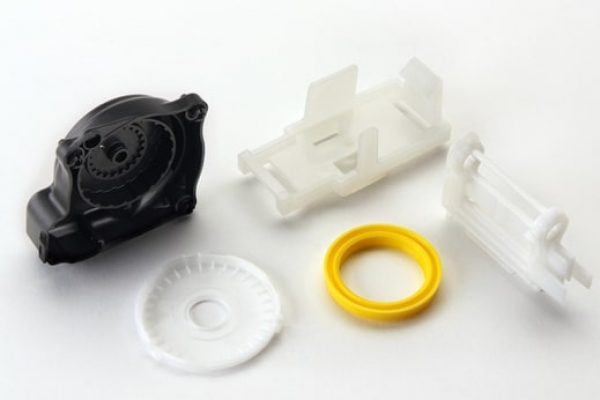

Our Advantages of CNC Machining
There are huge numbers of CNC machining service providers. Why should you choose us? Here are the top 3 reasons:
1. Experience
Our engineers have built up rich, deep experience from many previous projects, so they can handle complex and precision parts in several industries without a problem.
2. Advanced Equipment
XTJ has extensive in-house equipment for both manufacturing and testing. Your parts will be manufactured and inspected with our advanced in-house equipment, including HAAS 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC milling, Hexagon CMM, and Olympus XRF analyzer
3. Fast Turnaround
On average we return quotes within 24 hours, parts ship within 7 days or less, and we have a 99% on-time delivery and quality rate.
Our Injection Molding Capabilities
At XTJ, our experienced team produces injection molded products of the highest quality. We use injection molding in tandem with our rapid tooling capabilities, allowing us to create detailed custom parts quickly and efficiently. Our injection molding technology allows us to use a wide range of materials and finishes to suit the needs of any industry or application.
Here are some of the options you can choose from:

Plastic Injection Molding
The most popular process for plastics, thermoplastic injection molding is suitable for consumer products, automotive components, and everything in between.

Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding
Liquid silicone injection molding is ideal for creating detailed, temperature-resistant parts from thermosets liquid silicone, either alone or with overmolding.

Metal Injection Molding
Suitable for small and detailed metal parts, metal injection molding is cost-effective in large volumes and wastes less material than CNC machining.
Addition Injection Molding Options
Besides the basic injection molding services, we also offer two variants on the process – overmolding and insert molding. Both of these can be useful in specific situations.
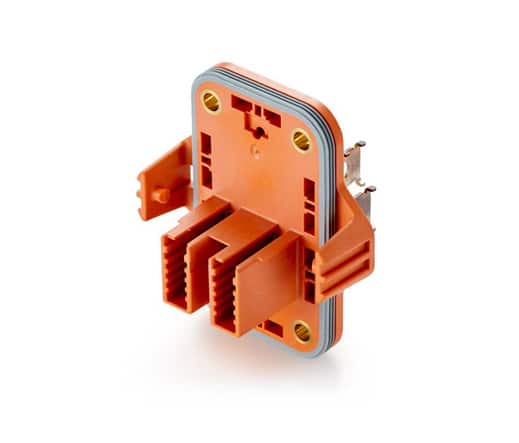
Overmolding
Overmolding uses injection molding to create a part from multiple materials. This process adds an injection-molded layer of material over an existing injection-molded workpiece. The overmolding process produces chemically bonded parts made using multiple materials.
The overmolding method is often cheaper and more effective than other manufacturing approaches that require creating and assembling component material parts separately. The process can also be used to build layered parts from scratch or to add a resistant outer layer to existing plastic parts and tools, providing a more rugged exterior. Toothbrushes consisting of a solid plastic body and rubberized grip are a common example of an overmolded product.
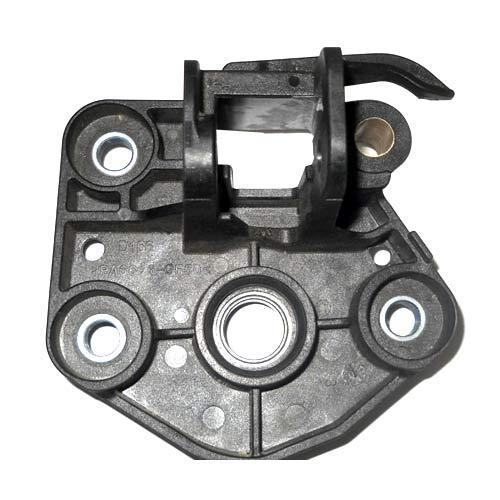

Insert Molding
Insert molding is similar to overmolding, but the substrate is not necessarily plastic and does not have to be produced via injection molding. For example, insert molding can be used to add a plastic coating to a pre-fabricated metal part.
Common parts made by insert molding include sharp handheld tools, such as scalpels, which consist of a metal blade partially housed within a plastic handle. Insert molding is also frequently used to create products that incorporate bushings, clips, and fasteners
Materials
- Acetal polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Nylon 66 (PA66)
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
- Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
- Glass-filled polycarbonate (PC-GF)
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE)
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Glass-filled, polyamide (PA-GF)
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- ABS polycarbonate (PC-ABS)
- Polymethyl methacrylate (acrylic) (PMMA)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV)


Finishing Options
- Acetal polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Nylon 66 (PA66)
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
- Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)
- Glass-filled polycarbonate (PC-GF)
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE)
Finishing Options
Injection molding is used to manufacture parts for a number of industries, including:
- Medical devices
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Electronic
- Packaging
- Food containers
- Toys
- Plastic prototypes
What is injection molding?
Plastic injection molding is the process of making plastic parts via the injection of molten plastic — typically a thermoplastic — into a metal mold, which is usually made from steel or aluminum.
The machine feeds raw material into the mold itself, the geometry of which is effectively a negative impression of the final part and which usually consists of two sections: an injection (A) mold and an ejector (B) mold.
The space between the two sections is the mold cavity, into which material is injected.
Although capable of producing a very wide range of parts, injection molding has some design constraints. Parts must have fairly narrow walls, should generally avoid overhanging features, and must have some degree of draft (tapered sides) so the part can be ejected from the mold.
Injection molding is principally used with plastics, and thermoplastics in particular. Thermoplastics are polymers that soften at an elevated temperature (at which point they can be freely injected into a mold) then return to a solid state after cooling. Injection molding also works with thermosets, which can be cured to make a solid but cannot then be melted back into a liquid state. Less common are elastomers.
Plastic Injection Molding FAQ
Injection molding can use almost any type of plastic that can also be combined together. This unmatched versatility is what makes injection molding so popular and suitable for some of the most demanding industries in the world. You can check out our selection of available materials and finishes on this page.
The plastic pellets are melted and are then inserted in liquid form into the mold tool, where it cools and takes the required shape. The process allows for high precision and tight tolerances because it can be replicated exactly each time.
Injection molding is one of the most affordable ways to manufacture large quantities of parts, especially for bigger production runs. Even though designing and creating the mold can take time, after that, the process becomes very affordable and efficient.
Before production can begin, we will first need to design the injection mold tool. How long this takes will depend on the complexity of your project, but the usual timeline can be as short as a week and as long as a couple of months.
